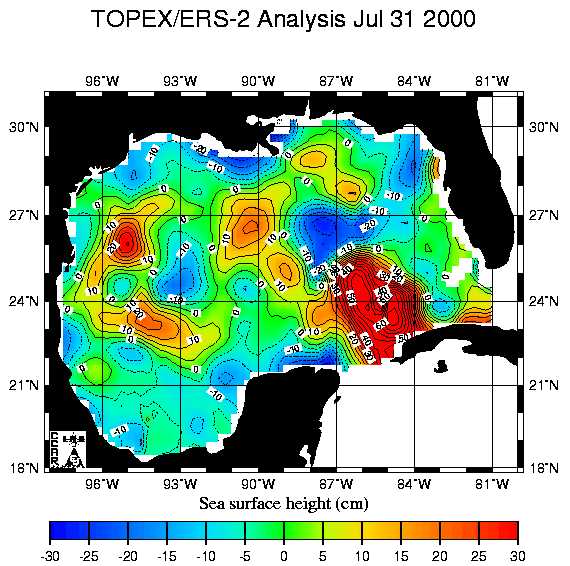
Figure 1. A display of sea surface height measured above or below a
time series mean.
Satellite Altimetry
Project Team Member(s)
LT David C. Dye, USN
Major Findings
Satellite altimetry is the measurement of sea surface height from a satellite. The precise orbit can be determined, and from that, changes in sea level may be ascertained. Measurements are routinely made with a root mean square (RMS) error of less than 5cm. TOPEX/POSEIDON and the ERS series of satellites have been providing altimetry data since the early 1990ís. Launched into Earth orbit in August 1992, TOPEX/POSEIDON enables early warnings of El Niño and La Niña weather patterns that have caused devastating floods in some areas and drier than normal periods in other places. A partnership between the U.S and France to monitor global ocean circulation, discover the tie between the oceans and atmosphere, and improve global climate predictions, the TOPEX/Poseidon satellite measures global sea level with unparalleled accuracy. The First and Second European Remote-Sensing Satellites (ERS-1 and ERS-2) were developed by the European Space Agency as a family of multi-disciplinary Earth Observation Satellites. They orbit the Earth in about 100 minutes and in 35 days have covered nearly every corner of the globe at least once. Both satellites are still in good health and provide a wealth of observations through their excellent suite of instruments. Applications for the data provided by these two systems include ship routing, commercial fishing, sport sailing, hurricanes, ocean circulation, marine mammals, shipboard research, climate forecasting, lobster larvae studies, and work on marine debris and coral reef health.
Another satellite systems called the GEOSAT Follow-on was launched in 1998, however, numerous technical and operator problems have plagued this system. Spurious resets and bad data have been recorded through this month. Testing began 22 Aug 2000 to continue through 24 Sep 2000, after which, the Navy expects the satellite will be ready for service.
A new satellite system is due to be launched at the end of the year
2000 or beginning of 2001 as the follow on to the highly successful TOPEX/
POSEIDON mission. Also a United States - French joint venture, the satellite
JASON will have instruments to include microwave radiometer, DORIS dual
frequency receiver, dual-frequency solid-state altimeter, GPS and a retro-reflector
array. Its mission will be improved studies of ocean and atmospheric characteristics
and their interrelation.
The most important aspects of jumbo eddies include:

Figure 1. A display of sea surface height measured above or below a
time series mean.
Website References
CCAR, Colorado Center for Astrodynamics Research. http://www-ccar.colorado.edu/
ESA, Earth Remote Sensing. http://earthnet.esrin.esa.it/
Delft Institute for Earth-Oriented Space Research. http://www.deos.tudelft.nl/
International LASER Ranging Service. http://ilrs.gsfc.nasa.gov/